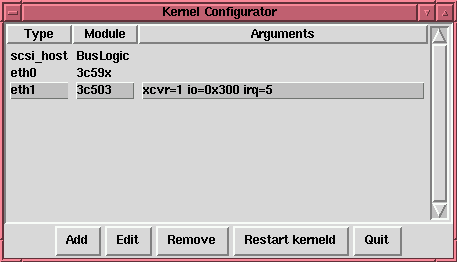
As discussed in Chapter 6, Red Hat Linux includes kerneld, the Kernel Daemon, which automatically loads some software and hardware support into memory as it is needed, and unloads it when it is no longer being used.
The tool shown in Figure 65 manages the configuration file for kerneld. While kerneld can load some things, such as filesystems, without explicit configuration, it needs to be told what hardware support to load when it is presented with a generic hardware request.

For instance, when the kernel wants to load support for ethernet, kerneld needs to know which ethernet card you have, and if your ethernet card requires special configuration, it needs to know about that, too.
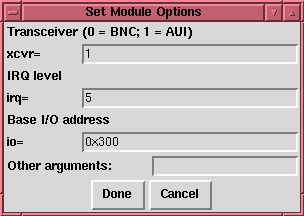
To change the options being given to a module when it is loaded, click on the line to select it, then click the Edit button. kernelcfg will bring up a window which looks like Figure 66 The options which kernelcfg knows about them (normally all available options) each have their own field. Normally, you will want to ignore the Other arguments field. Some modules normally take no arguments; just in case, they have an Arguments field which allows you to enter configuration information.
To change which module gets invoked to provide a generic service, such as an ethernet card or SCSI host adapter module, you need to delete the old one and add a new one. To delete a module, select it by clicking on it, then click on Delete. Then click on Add to add the new module, as explained in the following section.
If you have changed your SCSI controller (scsi_hostadapter), remember to make a new initial ramdisk with the /sbin/mkinitrd command as documented in section 6.1.2.
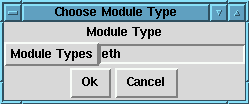
To add a module of any type, click on the Add button. You will be presented with a dialog box (Figure 67) asking you to choose a module type. Ethernet is eth, Token Ring is tr, SCSI controllers are scsi_hostadapter, and so on. Click OK to continue to
the next dialog box. If there is more than one module which can be used for the module type you have chosen, you will be presented with a dialog box (Figure 68) which asks which module you want to use, and may also ask for specifics about the type of module; for ethernet, for example, you need to choose from eth0, eth1, etc. When you are done, click OK again to continue to specify any module options in the next dialog box (Figure 68), which is the same as the dialog for editing a module.

The changes that you make with the Kernel Daemon Configuration tool will be made in the /etc/conf.modules file, which kerneld reads whenever it is started. Once you have made changes, you can restart kerneld by clicking on the Restart kerneld button. This will not cause any modules which are currently in use to be reloaded, it will only notify kerneld to use the configuration when it loads more modules in the future.