Chapter 13. Printer Configuration
Red Hat Linux no longer includes printtool. The printconf utility has replaced printtool. The printconf utility maintains the /etc/printcap configuration file, print spool directories, and print filters.
To use printconf, you must be running the X Window System and have root privileges. To start printconf, use one of the following methods:
On the GNOME desktop, go to the Main Menu Button (on the Panel) => Programs => System => Printer Configuration
On the KDE desktop, go to the Main Menu Button (on the Panel) => Red Hat => System => Printer Configuration.
Type the command printconf-gui at a shell prompt (for example, in an XTerm or a GNOME terminal). [1]
 | Do Not Edit /etc/printcap |
|---|---|
Do not edit the /etc/printcap file. Each time the printer daemon (lpd) is started or restarted, a new /etc/printcap file is dynamically created. |
If you want to add a printer without using printconf, edit the /etc/printcap.local file. The entries in /etc/printcap.local are not displayed in printconf but are read by the printer daemon. If you upgrade your system from a previous version of Red Hat Linux, your existing configuration file is converted to the new format used by printconf. Each time a new configuration file is generated by printconf, the old file is saved as /etc/printcap.old.
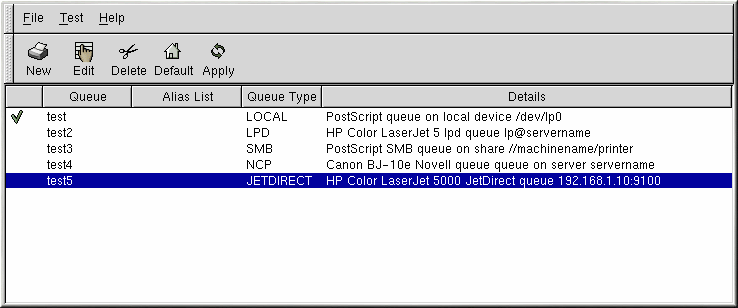
Five types of print queues can be configured with printconf:
Local Printer — a printer attached directly to your computer through a parallel or USB port. In the main printer list as shown in Figure 13-1, the Queue Type for a local printer is set to LOCAL.
Unix Printer (lpd Spool) — a printer attached to a different UNIX system that can be accessed over a TCP/IP network (or example, a printer attached to another Red Hat Linux system on your network). In the main printer list as shown in Figure 13-1, the Queue Type for a remote UNIX printer is set to LPD.
Windows Printer (SMB Share) — a printer attached to a different system which is sharing a printer over a SMB network (for example, a printer attached to a Microsoft Windows machine). In the main printer list as shown in Figure 13-1, the Queue Type for a remote Windows printer is set to SMB.
Novell Printer (NCP Queue) — a printer attached to a different system which uses Novell's NetWare network technology. In the main printer list as shown in Figure 13-1, the Queue Type for a remote Novell printer is set to NCP.
JetDirect Printer — a printer connected directly to the network instead of to a computer. In the main printer list as shown in Figure 13-1, the Queue Type for a JetDirect printer is set to JETDIRECT.
 | Important |
|---|---|
If you add a new print queue or modify an existing one, you need to restart the printer daemon (lpd) for the changes to take effect. |
Clicking the Apply button saves any changes that you have made and restarts the printer daemon. [2] Alternatively, you can choose File => Save Changes and then choose File => Restart lpd to save your changes and then restart the printer daemon.
If a printer appears in the main printer list with the Queue Type set to INVALID, the printer configuration is missing options that are required for the printer to function properly. To remove this printer from the list, select it from the list and click the Delete button.
Adding a Local Printer
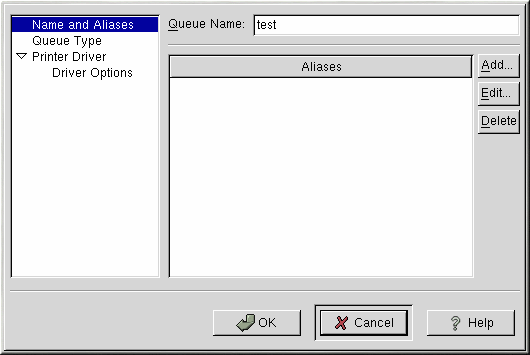
To add a local printer such as one attached to the parallel port or USB port of your computer, click the Add button in the main printconf window. The window shown in Figure 13-2 will appear.
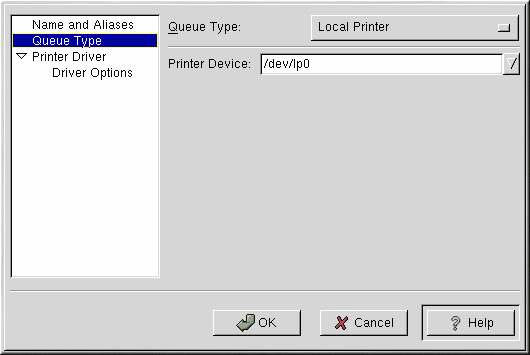
Enter a unique name for the printer in the Queue Name text field. This can be any descriptive name for your printer. You can also create alias names for the printer by clicking the Add button beside the Aliases list. Refer to the section called Creating Printer Aliases for more information about aliases. The printer name and aliases cannot contain spaces and must begin with a letter a through z or A through Z. The valid characters are a through z, A through Z, 0 through 9, -, and _.Click Queue Type from the left side menu and choose Local Printer from the Queue Type menu. Also enter the printer device in the Printer Device text field or choose it from the pulldown menu as shown in Figure 13-3.
Next, select the type of printer that is connected to the system by clicking Printer Driver from the left side menu. After choosing the manufacturer and model number of the printer, a list of drivers will appear. If there is more than one driver for the printer, choose the preferred driver in the Printer Driver list. If you are not sure which one to use, do not change this value. Click the Printer Notes button to view notes about the printer driver from the Linux Printing Database.
Click Driver Options from the left side menu after selecting a printer driver. These options will vary depending on the printer driver that you selected. Typical options include paper size, print quality, and printer resolution.
Click the OK button. The new printer will appear in the printer list in the main window. Click the Apply button in the main window to save your changes to the /etc/printcap configuration file and restart the printer daemon (lpd). After applying the changes, print a test page to ensure the configuration is correct. Refer to the section called Printing a Test Page for details.